The action allows reading the system event log and writing it into a CSV array. The information can be saved to a file or a variable. Each system log entry contains 16 fields. The list of fields and their types are provided below:
Category - integer CategoryString - string ComputerName - string Data – array of integer values EventCode – integer EventIdentifier – integer EventType – integer InsertionStrings – array of strings |
Logfile – string Message – string RecordNumber – integer SourceName – string TimeGenerated – datetime value TimeWritten - datetime value Type – string User – string |
More details about the structure of the system log can be found in the Microsoft documentation:
https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/previous-versions/windows/desktop/eventlogprov/win32-ntlogevent
Note about the datetime type:
The Date-Time value in the log is represented as a string in the format:
YYYYMMDDHHNNSS.ZZZZZZ±GGG
YYYY: 4-digit year
MM: 2-digit month
DD: 2-digit day
ZZZZZZ: 6 digits - microseconds
GGG: deviation of the time zone from GMT (Greenwich Mean Time) in minutes.
Log file
The source of the log. There are 3 options to choose from:
•Application
•Security – note that administrator privileges are required to read this log. Otherwise, you will get an empty list.
•System
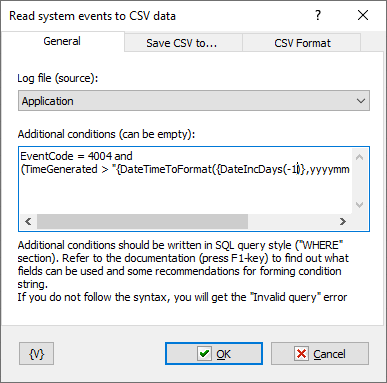
Additional conditions
You can use additional conditions. Conditions must be in the format of SQL query conditions. All log fields can be used in the condition. You can also use RoboTask variables in the condition.
For example:
(SourceName like "RoboTask%") and
(TimeGenerated > "{DateTimeToFormat({DateIncDays(-7)},yyyymmdd)}000000.000000-000")
Events related to RoboTask for the last 7 days.
Or
EventCode = 4004 and
(TimeGenerated > "{DateTimeToFormat({DateIncDays(-40)},yyyymmdd)}000000.000000-000")
Events with code 4004 for the last 40 days.
When using a field of type datetime in the condition, you must adhere to the string format. For example, as indicated in the provided examples.
Conditions can be as complex as needed. The main thing is to adhere to the SQL syntax. Failure to comply with the syntax will result in an "Invalid query" error.
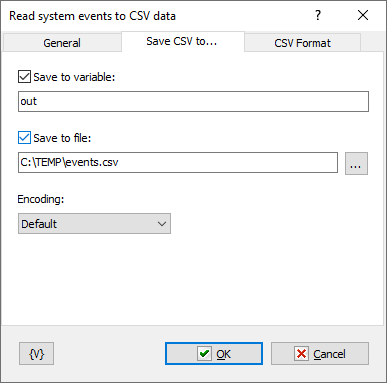
Save to variable
Turn this switch on and specify the variable name to save the CSV text.
Save to file
Turn this switch on and specify the file name to save the CSV text. Also, specify the text encoding if needed.
Note that UTF-8 is a universal format for any language.
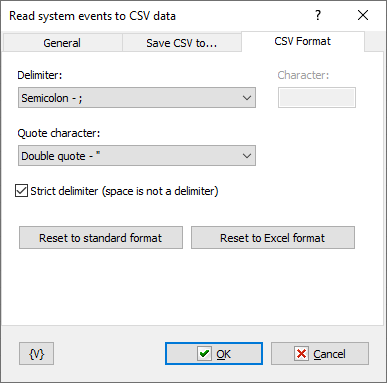
Specify the format of the CSV data: delimiter, quote character.
Note that if the "Strict delimiter" switch is not enabled, spaces are also considered delimiters. And all fields containing spaces must be enclosed in quotes.
Reset to standard format
Sets the standard parameters:
•Delimiter: Comma (,)
•Quotes: Double quotes (")
•Non-strict delimiter (spaces are also considered delimiters)
Reset to Excel format
Sets the parameters used by MS Excel by default:
•Delimiter: Semicolon (;)
•Quotes: Double quotes (")
•Strict delimiter.
![]() Related Topics
Related Topics
Note: This feature is available for Business license only |